Sun Safety
A DigitalNZ Story by National Library Services to Schools
The warmth of summer is a welcome relief after a long cold winter, but too much sun can be harmful. This story addresses some of the dangers, and how you can protect yourself from harmful UV rays on a hot summer day.
STAYING SAFE IN THE SUN
Kia hora te marino, kia whakapapa pounamu te moana, kia tere te kārohirohi i mua i tō huarahi
May peace be widespread, may the sea glisten like greenstone, and may the shimmer of light guide you on your way.
The sunny coast
Manatū Taonga, the Ministry for Culture and Heritage
BACKGROUND
New Zealand’s summer runs from December to February. At this time of the year, the days are longer and average temperatures can rise into the 30s. However, while we love spending time under the sun, we must remember that too much sun is also dangerous.
This story on sun safety contains the following:
- The sun
- The sun is important
- Damage from the sun
- Keeping us safe in the sun:
- Sunscreen
- Hats, umbrellas and shade
- Sunglasses
- Summer wear
- Drinking water
- Quick facts
- Glossary
- Bibliography
- Other resources
- Teaching and learning resources
- A gallery of images on sunhats
THE SUN
The sun is a star.
It is mainly made up of hydrogen and helium gasses.
It is in the centre of our solar system.
All the planets in our solar system revolve around the sun.
We cannot live on the sun because it is very hot.
FOR MORE ABOUT THE SUN
Cool facts about a hot place — is an article that has facts about the sun and how it affects us on Earth.
The sun — covers facts and details about the sun.
Sun — is an introduction to the sun at the centre of the solar system, what it is made up of, and what causes solar winds.
Sun facts for kids — covers history and important people who studied about the sun.
Why does the sun burn us — and other questions about the sun.
Tauranga New Zealand
Manatū Taonga, the Ministry for Culture and Heritage
THE SUN IS IMPORTANT
The sun gives us light and warmth.
Sunlight helps living things to grow.
Our skin uses sunlight to make vitamin D which strengthens our bones.
We can make electricity from the sun called solar energy.
FOR MORE ON THE IMPORTANCE OF SUNLIGHT
Photosynthesis — explains how plants capture sunlight.
Solar energy — what it is, how it is stored and used.
Vitamin D — helping your body through sensible sun exposure.
What causes the seasons? — the tilt of Earth’s axis and how it causes seasons.
George Ryan and a solar-powered lawnmower - Photograph taken by Ray Pigney
Alexander Turnbull Library
Sunflowers
iNaturalist NZ — Mātaki Taiao
Delicate Garden Skink
iNaturalist NZ — Mātaki Taiao
DAMAGE FROM THE SUN
Too much exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays can damage the skin, eyes and even cause melanoma, skin cancer. This can happen to people of any age or skin colour.
FOR MORE ON DAMAGE FROM THE SUN
About UV exposure and health — covers the pros and cons of UV exposure, the UV index and New Zealand’s UV levels.
How does sunburn happen? — explains how UVA and UVB rays can be damaging.
Most Melanomas Can Be Cured [poster]
Puke Ariki
Ultraviolet radiation
Manatū Taonga, the Ministry for Culture and Heritage
New Zealand highest rate of melanoma worldwide: RNZ Checkpoint
Radio New Zealand
KEEPING SAFE IN THE SUN
Sunscreen, protective clothing like hats, sunglasses, and summer clothes, and drinking plenty of water can keep us safe while we enjoy the sun.
SUNSCREEN
Sunscreen or sunblock is used to protect our skin from the sunburn. It can be in the form of a gel, cream, lotion or a spay. Sunscreen should:
· have an SPF (sun protection factor) of 30 or higher
· protect against UVA and UVB rays
· be water-resistant
Sunscreen should be applied well and regularly to be effective. Most packaging has directions on how to apply and how often sunscreen needs to be applied.
FOR MORE ABOUT SUNSCREEN
All about sunscreen — why we need it and how it works.
How to choose and use sunscreen — how, when and where to use sunscreen.
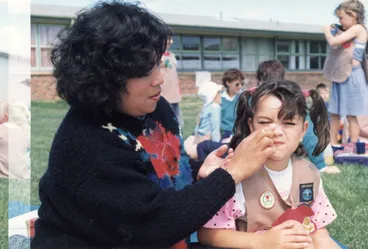
Pippin Kylie Neilson receives an application of sunblock from her Mum, Peka Neilson.
Upper Hutt City Library
Broad Spectrum Sunblock: Johnson & Johnson Sundown
Canterbury Museum
HATS, UMBRELLAS, AND SHADE
Wearing a hat or sitting under an umbrella or a shady tree is one of the best ways to stay out of direct sunlight. Wear a hat with a wide brim or a cap with flaps when outdoors to protect your eyes, ears, face and neck from the sun, even when the UV levels are said to be low.
Playing at the beach, 2006
Manatū Taonga, the Ministry for Culture and Heritage
Waipu Cove Beach Carnival
Auckland Libraries
Domain, Auckland City, New Zealand
Manatū Taonga, the Ministry for Culture and Heritage
SUNGLASSES
Wear sunglasses when outdoors on a bring sunny day to protect your eyes and the area around your eyes against harmful UV rays. Close fitting or wrap around sunglasses offer the best protection. The New Zealand Association of Optometrists (NZAO) has lots of advice on why we need sunglasses.
Child wearing pink framed sunglasses
Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa
Sunglasses, military
Puke Ariki
SUMMER WEAR
Clothes can absorb or block harmful UV rays, so choosing the right kind of clothes will help protect you from harmful sunlight. Dark or bright colours, and denim, canvas and wool offer better protection than lighter shades and loosely woven cloth. It’s better to wear long-sleeves and long pants as this will offer better protection.
FOR MORE ON PROTECTIVE SUMMER WEAR
Sun protective clothing — has lots of advice on the selecting the most effective sun protective summer wear.
Pleasant days at the seaside
Auckland Libraries
Keeping up with the kaftans dress
New Zealand Fashion Museum
DRINKING WATER
Our bodies sweat and lose water when we play outside on a hot sunny day. This is called dehydration and it can make us feel thirsty, dizzy, tired and very ill. This is why we need to keep drinking lots of water when playing outdoors and during sports activity.
FOR MORE ON DEHYDRATION
Dehydration — covers signs and reasons for dehydration and how to prevent it.
Dehydration — key points, symptoms, causes and treatment of dehydration.
Children drinking from a water fountain, 1951
Manatū Taonga, the Ministry for Culture and Heritage
Label
Te Aroha & Districts Museum
QUICK FACTS
· Ultraviolet light is invisible to the human eye, but some insects like bumblebees can see it.
· The ultraviolet index or UV index is an international standard for measuring the strength of ultraviolet rays at a particular place and time.
· The World Health Organisation measures UV levels on a scale from 0 (low) to 11+ (extreme). Sun protection is recommended when the UV levels are 3 (moderate) or higher.
· The sun's UV rays are the main cause of skin cancer.
· UV levels in New Zealand are highest during summer but can also be somewhat high in spring and autumn.
· In New Zealand UV levels are monitored by NIWA. You can get a daily UV index reading from NIWA.
· You can get sunburn on a ski field because snow reflects UV radiation. This is why skiers use sunscreen and sunglasses.
· SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor. The number beside it indicates how well the sunscreen will protect your skin against sunburn. The higher the SPF number the better the protection, provided you have applied the sunscreen properly.
· No sunscreen offers complete protection against UV radiation, so you need to limit your time spent in the sun.
· Apply and reapply sunscreen to all parts of the body such as the face, neck, ears, arms, legs, and back every two hours, especially after a swim.
GLOSSARY
Definitions below have been taken from the Oxford Learner's Dictionary.
axis— an imaginary line through the centre of an object, around which the object turns.
certified — to state officially, especially in writing, that something is true.
exhaustion— the state of being very tired.
exposure— the state of being in a place or situation where there is no protection from something harmful or unpleasant.
heatstroke— an illness with a high temperature and often loss of consciousness, caused by being in too great a heat for too long.
intensity — the strength of something, for example, light.
immune system — the system in your body that produces substances to help it fight against infection and disease.
mandatory— required by law.
melanin— a dark substance in the skin and hair that causes the skin to change colour in the sun’s light.
melanoma— a type of cancer that appears as a dark spot or tumour on the skin
radiates — if something radiates heat, light or energy or heat, etc. radiates from it, the heat is sent out in all directions.
tanning — if a person or their skin tans or is tanned, they become brown as a result of spending time in the sun.
UVA — ultraviolet rays that are relatively long.
UVB — ultraviolet rays that are relatively short.
wrinkling — the process by which wrinkles form in the skin.
This story was curated and compiled by Te Puna Mātauranga o Aotearoa | National Library of New Zealand, Services to Schools staff, January 2021.
Church picnic at Snell's Beach
Auckland Libraries
Beach picnic, Northland
Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Use our lending service to order these books and other related topics associated with fire safety.
NON-FICTION
Kapai's sunsmart rules: be a stay alive kiwi by Uncle Anzac, 2003 (primary).
Max and Mila at the beach: a fun guide to teaching your child about skin cancer, melanoma and sun safety by Amalyn Persohn Marti, 2013 (primary).
Staying safe in the sun by Siân Smith, 2013 (primary).
Sunburn by Sharon Gordon, 2002 (primary).
Why do I get sunburn?: and other questions about skin by Angela Royston, 2002 (primary).
OTHER RESOURCES
EPIC databases — Find more information on this topic on EPIC. Databases recommended are Britannica School Primary and Elementary (Gale in Context). School login may be needed.
How to be safe when you’re in the sun — has tips on how to enjoy the sun and still be safe.
Safety outdoors — is all about facts about the sun, sun safety and what to do if you get sunburned.
Stay SunSmart in March — has articles, facts, ideas and resources to keep in mind for summer, and when UV levels remain high even in March in New Zealand.
Sun safety — has tips on how to protect yourself from the sun, selecting sunscreen and the pros and cons of being out in the sun.
Sun safety — has links for sun safety information for the public, workplaces and schools.
Sun safety — from KidsHealth has advice on to protect skin form melanoma and skin damage from too much sun.
Sunsmart — this New Zealand website has all you need to know about sun protection and checking for skin cancer.
What happens when you get heat stroke? — a video to explain what happens to the body and an action plan in case anyone suffers from heat stroke.
When to be SunSmart — is advice from the Cancer Society of New Zealand on what to do to protect yourself, your whānau and your community from harmful UV radiation.
TEACHING AND LEARNING RESOURCES
Be sunSmart — this lesson plan teaches why the sun is needed by humans, plants and animals, how it can be harmful and how to protect ourselves from it.
Care in the sun — is a teaching pack that offers ideas to make it easy to integrate information on car in the sun into the curriculum.
A summer safety activity — children develop social and language skills while practising sun safety.
Safe and fun, in the sun — helps children and young people understand how to keep their skin safe in the sun.
Sunsmart schools — from Cancer Society for teachers, students and parents on how to be SunSmart.
Sun Smart [poster]
Puke Ariki
Sun Block: Hawaiian Tropic
Canterbury Museum
Parasol
Howick Historical Village
A GALLERY OF IMAGES ON SUNHATS
Hats, especially broad-brimmed ones, are enjoying a revival in the 2000s as people become conscious of the health risks of too much exposure to the sun.
Source: Hats, footwear and oilskins — Rural clothing, Te Ara - The Encyclopedia of New Zealand.
Hat Sun
MOTAT
bonnet
Auckland War Memorial Museum Tāmaki Paenga Hira
Sun Hat: Sir Edmund Hillary
Canterbury Museum
sun-shield
Auckland War Memorial Museum Tāmaki Paenga Hira
Women's sun hat
Waikato Museum Te Whare Taonga o Waikato
Hat Sun
MOTAT
bonnet, sun
Auckland War Memorial Museum Tāmaki Paenga Hira
bonnet, sun
Auckland War Memorial Museum Tāmaki Paenga Hira
Small Chinese Girl In Hong Kong.
Presbyterian Church of Aotearoa New Zealand
hat, sun
Auckland War Memorial Museum Tāmaki Paenga Hira
Women's sun hat
Waikato Museum Te Whare Taonga o Waikato
St Joseph's School; sun hats added to school uniform.
Upper Hutt City Library





![Most Melanomas Can Be Cured [poster] Image: Most Melanomas Can Be Cured [poster]](https://images.digitalnz.org/TCHjVj2laDH7ffwsJ1ooxZOxOF4=/368x0/https%3A%2F%2Fcollection.pukeariki.com%2Frecords%2Fimages%2Flarge%2F81589%2Fee7fd1ba0f8b86c9a306e1afcbafdba29d95b8d9.jpg)



















![Sun Smart [poster] Image: Sun Smart [poster]](https://images.digitalnz.org/dIIxxMXBa98_JeFdZrDl_MHfgOQ=/368x0/https%3A%2F%2Fcollection.pukeariki.com%2Frecords%2Fimages%2Flarge%2F81591%2F5e744c2c463f9ebf0262444e024c3ed582e996b9.jpg)













